Sphinginae subfamily
Sphingini tribe:
 |
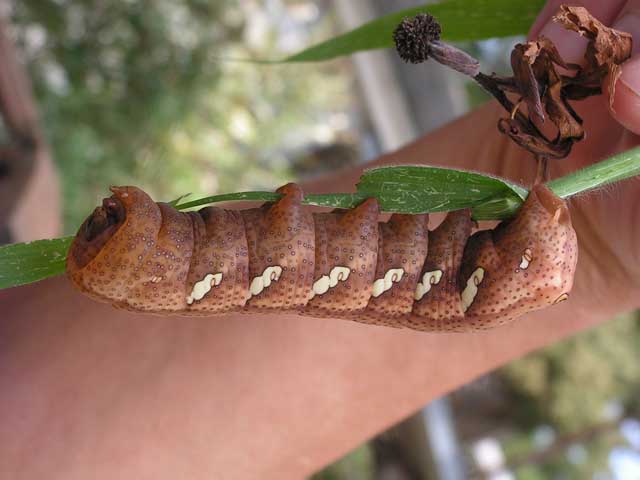
Ceratomia amyntor
BAMONA, Elm Sphinx, Four-horned Sphinx:
Elm (Ulmus), birch (Betula), basswood (Tilia), and cherry (Prunus).
There are both green and brown forms. The four horns near the head are diagnostic.
|
 |
Ceratomia catalpae BAMONA, Catalpa Sphinx:
Young caterpillars feed gregariously on Catalpa species (Catalpa bignoniodes and C. speciosa) in
Bignoniaceae family, skeletonizing foliage. Mostly white in early instars.
|
 |
Ceratomia hageni BAMONA, Hagen's Sphinx, Osage Orange Sphinx:
Larvae feed on osage orange (Maclura pomifera), and they have a granulous appearance with variable amounts of purple along the oblique white stripes.
|
 |
Ceratomia undulosa BAMONA, Waved Sphinx:
Fraxinus, Ligustrum, Quercus, Crataegus and Chionanthus virginicus.
Fifth instar, spiracular ovals are decidedly red and anal horn is off-white to pinkish laterally.
|
 |
Lintneria eremitus BAMONA, Hermit Sphinx:
Note triangular bump on the thorax. Larval hosts are various species of beebalm (Monarda), mints (Mentha), bugleweed (Lycopis), and sage (Salvia).
|
 |
Manduca jasminearum WO, Ash Sphinx:
Larvae feed on ash in the Fraxinus genus. Syringa and Ulmus have also been reported. Note the black anal horn.
|
 |
Manduca quinquemaculatus BAMONA, Five-spotted Hawkmoth:
Tomato Hornworms: black horn at the end of the abdomen. Larvae feed on potato, tobacco, tomato, and other plants in the nightshade family (Solanaceae).
|
 |
Manduca rustica WO, Rustic Sphinx:
Note the green horn, raised white bumps and strong dark lines anterior to the white ones.
|
 |
Manduca sexta BAMONA, Carolina Sphinx:
Tobacco Hornworms, red-tipped horn at end of abdomen; true gluttons; feed on tobacco and tomato, occasionally potato and pepper crops, other plants in
nightshade family (Solanaceae).
|
 |
Paratrea plebeja BAMONA, Plebeian Sphinx:
Common trumpetcreeper (Campsis radicans), Florida yellow-trumpet (Tecoma stans), lilac (Syringa species),
passionflower (Passiflora species). Anal horn is blue, preceded by yellow dash.
|

| Sphinx canadensis BAMONA, Canadian Sphinx:
Uncommon at lights, not often reported anywhere.
Exclusively black ash (Fraxinus nigra). Variable appearance but always with granulous (darker protrusions) on pinkish horn.
|
 |
Sphinx chersis BAMONA, Northern Ash Sphinx, Great Ash Sphinx:
Pale bluish green. Head: pair of yellow lateral bands meeting at apex. Oblique, lateral stripes pale, bordered anteriorly with darker green.
Ash, lilac, privet, cherry, quaking aspen.
|
 |
Sphinx drupiferarum BAMONA, Wild Cherry Sphinx:
Larvae hide by day, feed primarily on cherry, plum, apple at night. Amelanchier nantuckensis in Massachusetts; Michigan on
Prunus serotina. Note purple oblique lines.
|
 |
Sphinx franckii WO, Franck's Sphinx Moth:
Larvae feed exclusively on various species of ash (Fraxinus). Raised, pointed bumps, especially near the head and thorax give this caterpillar a reptilian appearance.
|
 |
Sphinx gordius WO, Apple Sphinx:
Apple (Malus), sweetfern (Myrica), Carolina rose (Rosa carolina), blueberry, huckleberry
(Vaccinium), white spruce (Picea glauca), American larch (Larix laricina), alder (Alnus).
|
 |
Sphinx kalmiae WO, Laurel Sphinx:
In the final instar, the black on the head, lateral lines, horn and on abdominal legs is diagnostic. Larvae feed primarily on lilac and fringe.
|
 |
Sphinx vashti WO, Snowberry Sphinx:
Common snowberry (Symphoricarpos albus) and on coralberry (S. orbiculatus). Note two golden
lines of slightly raised bumps, one just behind head, other
on thorax.
|
Smerinthini Tribe:
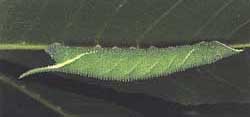 |
Amorpha juglandis BAMONA, Walnut Sphinx:
Walnut, butternut (Juglans), hickory (Carya), alder (Alnus), beech (Fagus), hazelnut (Corylus), hop-hornbeam (Ostrya).
|
 |
Paonias excaecata BAMONA, Blinded Sphinx:
Larvae accept willows, birches, and cherries. I have also found them in the wild on oak in eastern Canada.
|
 |
Paonias myops BAMONA, Small-eyed Sphinx:
Wild cherry species are the favorites as larval foodplants, but eggs will also be deposited on birches and other forest trees.
There are varying degrees in the amount of red markings along the sides.
|
 |
Smerinthus jamaicensis BAMONA, Twin-spotted Sphinx:
Birches, cherries, expecially fond of poplars, willows. Red markings on sides
vary greatly from specimen to specimen.
|
 |
Smerinthus cerisyi
WO??, Cerisy's Sphinx:
Pale green, granular skin, pale lateral diagonal lines, faint red
spiracular circles, very pale longitudinal lines running from head to more pronounced anal diagonal line.
Green heads bounded dorsally with pale yellow inverted V. usualy further north
|
Macroglossinae subfamily
Dilophonotini Tribe:
Aellopos titan, Titan sphinx, BAMONA. This species would occur in Benton only as an adult stray from
further south.
 |
Hemaris diffinis BAMONA, Snowberry Clearwing:
Snowberry (Symphoricarpos), honeysuckle (Lonicera), Coralberry, viburnums, Blue Dogbane (Apocynum), dwarf bush honeysuckle (Diervilla
lonicera). Horn: black, yellow base.
|
 |
Hemaris thysbe BAMONA, Hummingbird Clearwing:
There is also an orangey-pink prepupal form. The lateral line runs
from S1 to the blue horn. Viburnum, related plants.
generally more eastern species
|
Philampelini Tribe:
 |
Eumorpha achemon JM/BAMONA, Achemon Sphinx:
Grape (Vitis), Virginia Creeper (Parthenocissus quinquefolia), other vines, ivies
(Ampelopsis). Both light (green) form and darker (tan/brown) form. Note six "segmented" oblique lines.
|
Eumorpha achemon, fifth instar, Warsaw, September 8, 2013, Janet Manson.
 |
Eumorpha pandorus BAMONA, Pandorus Sphinx:
If you have Grape or Virginia Creeper nearby, then you might encounter
this species. Note five large white ovals. Orangey-brown and green forms also.
|
Macroglossini Tribe:
 |
Amphion floridensis BAMONA, Nessus Sphinix:
In additon to Virginia creeper larvae accept Grape (Vitis), ampelopsis (Ampelopsis), and cayenne pepper (Capsicum).
Larvae are green until the final instar.
|
 |
Darapsa choerilus BAMONA, Azalea Sphinx:
Azalea, Viburnum; progress rapidly. Larva, left, on Viburnum cassinoides, ready to
pupate. Color change from green to light burgundy-brown indicates imminent pupation. |
 |
Darapsa myron BAMONA, Virginia Creeper Sphinx, Grapevine Sphinx:
If you have foodplants indicated in common names, you probably have this
species. Lower wings orange. Virginia creeper (Parthenocissus quinquefolia),
Grape (Vitis), Ampelopsis, Viburnum. |
 |
Deidamia inscriptum WO, Lettered Sphinx:
Grape (Vitis), ampelopsis (Ampelopsis),
Virginia creeper (Parthenocissus). The alternating yellow and greyish-green rings across the back distinguish this larva.
|
 |
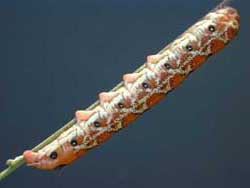
Hyles lineata BAMONA, White-lined Sphinx:
Highly varied; willow weed (Epilobium), four o'clock (Mirabilis),
apple (Malus), evening primrose (Oenothera), elm (Ulmus), grape (Vitis), tomato (Lycopersicon),
purslane (Portulaca), Fuschia. Red/black swellings split by dorso-lateral lines.
|
 |
Proserpinus juanita WO, Juanita Sphinx:
Newly-hatched caterpillars eat eggshells. (Onagraceae) including evening primrose (Oenothera), gaura (Gaura),
and willow weed (Epilobium). Michael Van Buskirk has found them on Guara biennis in Missouri. rare
|
 |
Sphecodina abbottii BAMONA, Abbott's Sphinx:
Larvae feed at night on grape (Vitis), ampelopsis (Ampelopsis); hide on bark in day. Virginia creeper. Also dark form
without green patches. Note "raised eye", replacing the anal horn.
|
 |
Xylophanes tersa, BAMONA, Tersa Sphinx:
Snake-like head and three thoracic segments may retracted into abdominal segment 1, swollen, adorned with pair of light-ringed eye-spots.
Voracious appetites for garden penta species. Green and brown forms both occur.
|
|
|



